Infant dehydration
SYMPTOMS
What is Pediatric Dehydration?
Under normal circumstances, the amount of water entering and leaving the body is roughly balanced, maintaining a dynamic equilibrium of water content in the body.
Pediatric dehydration refers to a state where a child's body lacks sufficient water. It can be caused by inadequate water intake or excessive water loss.
Children have a higher demand for water, with body fluids accounting for 65%–78% of their body weight, making them more prone to dehydration than adults.
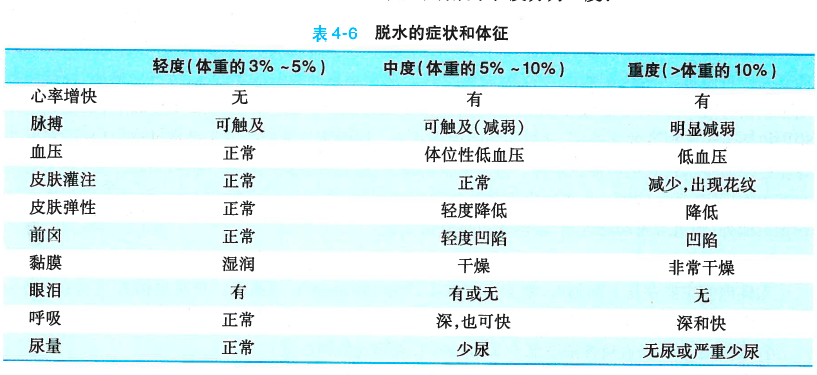
Is Pediatric Dehydration Classified by Severity?
Yes. Based on the proportion of lost body weight due to fluid loss, dehydration can be simply categorized into mild, moderate, and severe levels.
What Are the Symptoms of Pediatric Dehydration?
Dehydration can lead to dry skin, cracked lips, sunken eyes, reduced tear production, loss of skin elasticity, decreased urine output, and rapid breathing.
Severe dehydration may also include mottled skin, cold limbs, confusion, and other symptoms.
Long-term dehydration may manifest as weight loss.
TREATMENT
How to relieve or alleviate dehydration in children?
When signs of dehydration are noticed in a child, first assess whether the child can eat or drink.
-
If the child can eat or drink, ensure adequate fluid intake. For infants, increase the frequency of breastfeeding. Older children should drink more water, but plain water alone is not sufficient—salt intake must also be replenished. The best method is to use Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS) III. ORS III is a pre-mixed combination of electrolytes and glucose that, when dissolved in water, replenishes fluids, salts, and sugars. After preparing ORS III according to the instructions, administer it to the child in small, frequent doses. The prepared solution can be stored in a water bottle or feeding bottle.
-
If the child is in a high-temperature environment, loosen their clothing and move them to a cooler place.
-
If the child has significant diarrhea and loses excessive fluids, oral administration of montmorillonite powder can help alleviate diarrhea and reduce fluid loss.
-
If the above methods do not improve symptoms, or if the child is unable to eat or drink independently, seek medical assistance promptly.
DIAGNOSIS
When should a child with dehydration seek medical attention at a hospital?
Seek immediate medical care in the following situations:
- The child shows signs of dehydration and is unable to eat or drink, vomiting immediately after drinking.
- The child exhibits severe dehydration symptoms, such as cold hands and feet, mottled skin, lethargy (reduced activity, no crying or fussing, fatigue), or urine output reduced by more than half compared to usual.
- The child has uncontrollable diarrhea with repeated watery stools, indicating worsening dehydration.
- The child experiences seizures or loss of consciousness.
POTENTIAL DISEASES
What are the possible causes of dehydration in children?
Gastroenteritis, heatstroke, etc., are the main causes of dehydration. Less common causes include ketoacidosis, kidney abnormalities, medications, and improper feeding.
- Gastroenteritis: Can cause persistent vomiting and diarrhea in children, a common cause of dehydration. Viral gastroenteritis is more prevalent in autumn and winter, while bacterial gastroenteritis is more common in summer due to food spoilage.
- Excessive heat: Such as summer heatstroke or being left in a hot car. High temperatures can lead to significant fluid loss through the skin, causing dehydration.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis: An acute complication of diabetes, often seen in children with type 1 diabetes, which can also lead to dehydration.
- Kidney disease: The kidneys primarily regulate fluid excretion. Kidney disorders may cause excessive fluid loss, leading to dehydration if not replenished.
- Medication misuse: Certain drugs, such as diuretics or dehydrating agents, may also induce dehydration.
- Improper feeding: Incorrect formula preparation for infants over time can disrupt water metabolism, resulting in dehydration.
